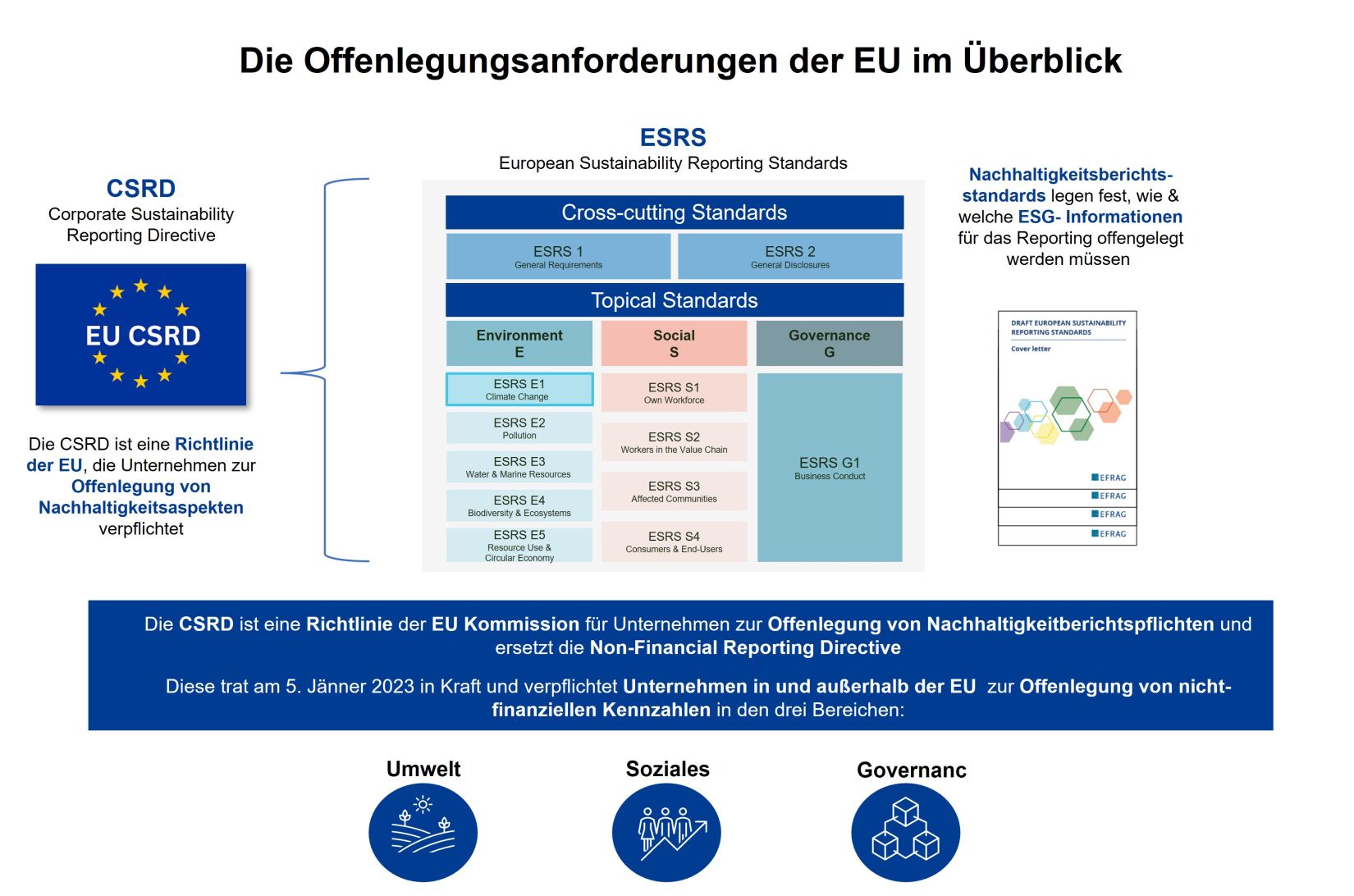
Reporting on the cross-cutting standards, as well as ESRS E1 "Climate Change" and ESRS S1 "Own Workforce," is mandatory for all companies. All other standards must be reported if they are considered relevant to the company.
The ESRS basically covers the following topics:
Sustainability policy
Companies must outline specific policies regarding a range of sustainability issues – environmental protection, treatment of employees, corporate and company diversity, social responsibility, human rights, anti-corruption and anti-bribery – and describe the company's internal procedures for monitoring and enforcing these policies.
Sustainability goals
Companies must develop and report on their sustainability targets, progress towards achieving their targets and how these targets align with a transition to a sustainable economy in general and with achieving net-zero emissions by 2050 in particular (as stipulated by existing EU legislation).
Value and supply chains
Companies must disclose their process for identifying the social and environmental impacts in their value chains and supply chains.
Sustainability risks
Companies must document the risks that various sustainability issues (e.g., climate change, use of fossil fuels, or dependence) pose to the company.
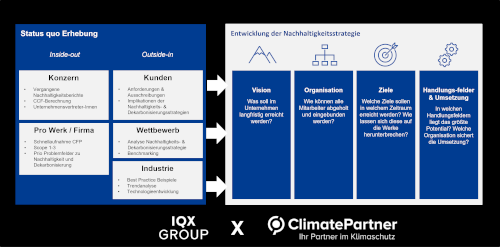
Get involved in corporate sustainability and actively contribute to future-proof development. Take advantage of the opportunity to find an efficient and cost-effective entry point into this field together with us and our partner ClimatePartner.
Our comprehensive approach goes beyond CSRD requirements. We offer not only support in calculating the CO2 footprint and developing a sustainability strategy, but also expertise in the rapid implementation of decarbonization plans from the product development process to the finished product.
Ensure compliance with legal requirements and strive for continuous improvement. A sustainability-oriented corporate culture can support the environment and is also key to long-term success. Are you interested in the comprehensive integration of a sustainability strategy? Then get in touch with us.